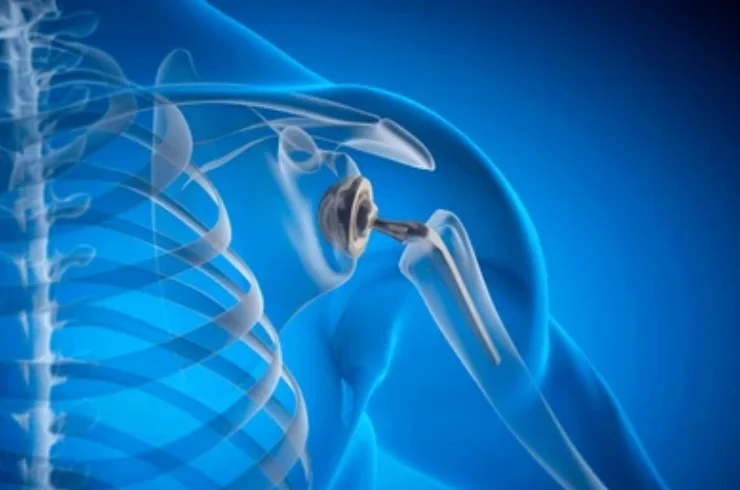
Shoulder Replacement: A Comprehensive Guide
Shoulder replacement surgery, or shoulder arthroplasty, involves removing a damaged shoulder joint and replacing it with an artificial joint (prosthesis). It is primarily performed to relieve pain and restore function in individuals with severe shoulder issues, often due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or rotator cuff tears.
The procedure includes several types, such as total shoulder replacement, reverse shoulder replacement, and partial shoulder replacement, based on the specific condition. The surgery involves anesthesia, making an incision, and implanting the prosthetic components. Recovery typically involves a hospital stay, pain management, and physical therapy to regain mobility. Potential risks include infection, blood clots, dislocation, and implant failure. Long-term management emphasizes rehabilitation, regular follow-ups, and lifestyle adjustments for optimal outcomes.